
Manganese Steel is a key material in heavy industry, known for its exceptional strength, toughness, and wear resistance that few materials can match. High Mn Steel, including Manganese Steel Plates and Manganese Steel Castings, ensures machinery operates efficiently even under extreme conditions. Companies experience up to 23% improved performance and extended service life, as illustrated below:
Key Takeaways
- Manganese steel is extremely strong and tough because of its high manganese content, which helps it get harder when hit or pressed.
- This steel resists wear, impact, and corrosion better than many other steels, making it ideal for heavy industry machines that face rough conditions.
- Industries like mining, construction, and railways rely on manganese steel to keep equipment safe, durable, and running longer with less repair.
Manganese Steel: Composition and Unique Features

What Sets Manganese Steel Apart
Manganese steel stands out because of its special mix of elements. Most types contain about 10-14% manganese and 1-1.4% carbon, with the rest being iron. Some high-manganese steels used in mining or railways can have up to 30% manganese. This high manganese content gives the steel its famous strength and toughness. Scientists have found that manganese changes how the steel forms and transforms. It helps the steel stay strong and tough, even when it faces hard hits or heavy loads.
Material science research shows that manganese steel has a unique microstructure. When the steel bends or stretches, tiny changes happen inside. These changes, called TWIP and TRIP effects, help the steel get even stronger without breaking. The steel can also keep its strength in temperatures from –40 to 200 °C.
The table below shows the typical composition of manganese steel compared to other steels:
| Alloying Element | Typical Percentage Composition (wt%) | Range or Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Carbon (C) | 0.391 | Typical manganese steel plate |
| Manganese (Mn) | 18.43 | Typical manganese steel plate |
| Chromium (Cr) | 1.522 | Typical manganese steel plate |
| Manganese (Mn) | 15 – 30 | High-manganese steels |
| Carbon (C) | 0.6 – 1.0 | High-manganese steels |
| Manganese (Mn) | 0.3 – 2.0 | Other alloy steels |
| Manganese (Mn) | >11 | Austenitic steels for high wear resistance |
Comparison with Other Steels
Manganese steel performs better than many other steels in tough jobs. It has higher tensile strength and can handle more impact. The steel also gets harder when it is hit or pressed, which helps it last longer in harsh places like mines or railways.
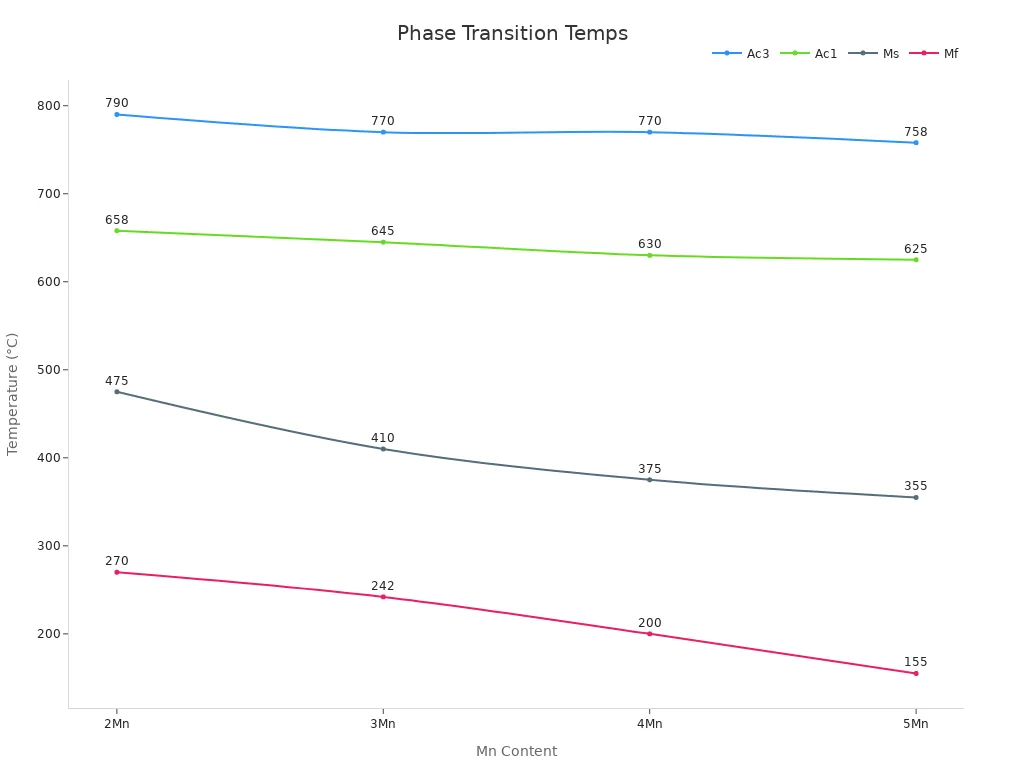
The chart below shows how manganese content affects the steel’s strength and phase changes:
When compared to stainless steel, manganese steel has better impact resistance and wear resistance. Stainless steel resists rust better, but manganese steel is the top choice for places where equipment faces lots of hits and scrapes.
Tip: Manganese steel is hard to machine because it gets tougher as you work on it. Workers often use special tools to cut or shape it.
Key Properties of Manganese Steel in Industry
Impact and Abrasion Resistance
Manganese steel stands out for its ability to handle hard hits and rough treatment. In heavy industry, machines often face rocks, gravel, and other tough materials. When these materials strike or scrape against metal, most steels wear down quickly. Manganese steel, however, gets stronger with each impact. This happens because its structure changes under pressure, making the surface harder while keeping the inside tough.
Researchers tested manganese steel by hitting it with a tungsten-carbide striker in a lab. They added sharp iron particles to make the test even tougher. The steel held up well, showing little wear even after repeated impacts. In another test, engineers used jaw crushers to grind gravel. The manganese steel jaws lost less mass and stayed smoother than other steels. Scientists found tiny grains and special patterns inside the steel after these tests. These changes help the steel resist both cutting and denting.
Did you know? Manganese steel gets harder the more it works. This “work hardening” makes it perfect for mining, quarrying, and crushing equipment.
Engineers also use manganese steel coatings on parts that slide or rub together, like railway tracks and coalcutter guides. These coatings last longer and resist damage from heavy loads and constant movement. The secret lies in the mix of elements and the way the steel changes when stressed.
Durability and Toughness
Durability means a material can last a long time, even when used every day. Toughness means it can take a hit without breaking. Manganese steel scores high in both areas. Lab studies show that medium manganese steel can stretch over 30% before breaking and has a tensile strength above 1,000 MPa. This means it can bend and flex without snapping.
When machines run for hours or days, their parts face repeated stress. Manganese steel handles this well. Tests show that it resists cracks and delays damage, even when loaded again and again. Scientists use special models to predict how the steel will behave over time. These models show that manganese steel adapts to stress, spreads out damage, and keeps working longer than many other metals.
- Comparative durability tests highlight manganese steel’s toughness:
- Hardness and impact strength tests show that high-vanadium manganese steels beat traditional Hadfield steel.
- Pin-on-disk and ball mill tests prove that manganese steel resists wear better than other high-strength alloys.
- Tensile tests reveal that alloyed manganese steels stay strong and flexible, even at different speeds of stretching.
- Adding elements like chromium, tungsten, and molybdenum makes the steel even tougher and more resistant to wear.
Note: The special structure of manganese steel helps it absorb energy and slow down cracks. This keeps machines running safely and reduces the need for repairs.
Corrosion Resistance
Corrosion happens when metal reacts with water, air, or chemicals and starts to break down. In places like mines or near the sea, corrosion can ruin equipment fast. Manganese steel offers good protection, especially when treated with extra elements like molybdenum or chromium. These elements help form a thin, stable layer on the steel’s surface. This layer blocks water and chemicals, slowing down rust and other damage.
Lab tests show that manganese steel with molybdenum and special heat treatments resists corrosion much better. Scientists use microscopes to see these protective layers. They also run electric tests to measure how fast the steel corrodes. The results show that treated manganese steel lasts longer in harsh places.
However, in very acidic spots, manganese steel can still face problems like pitting or cracking. That’s why engineers often add more elements or use special treatments to boost its resistance.
The table below compares how fast different steels corrode in a marine environment:
| Corrosion Duration (hours) | 24 | 72 | 168 | 288 | 432 | 600 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 9Ni steel | 0.72 | 0.96 | 0.67 | 0.65 | 0.63 | 0.60 |
| Medium-Mn steel | 0.71 | 0.97 | 1.42 | 1.08 | 0.96 | 0.93 |
| High-Mn steel | 0.83 | 1.38 | 1.73 | 0.87 | 0.70 | 0.62 |
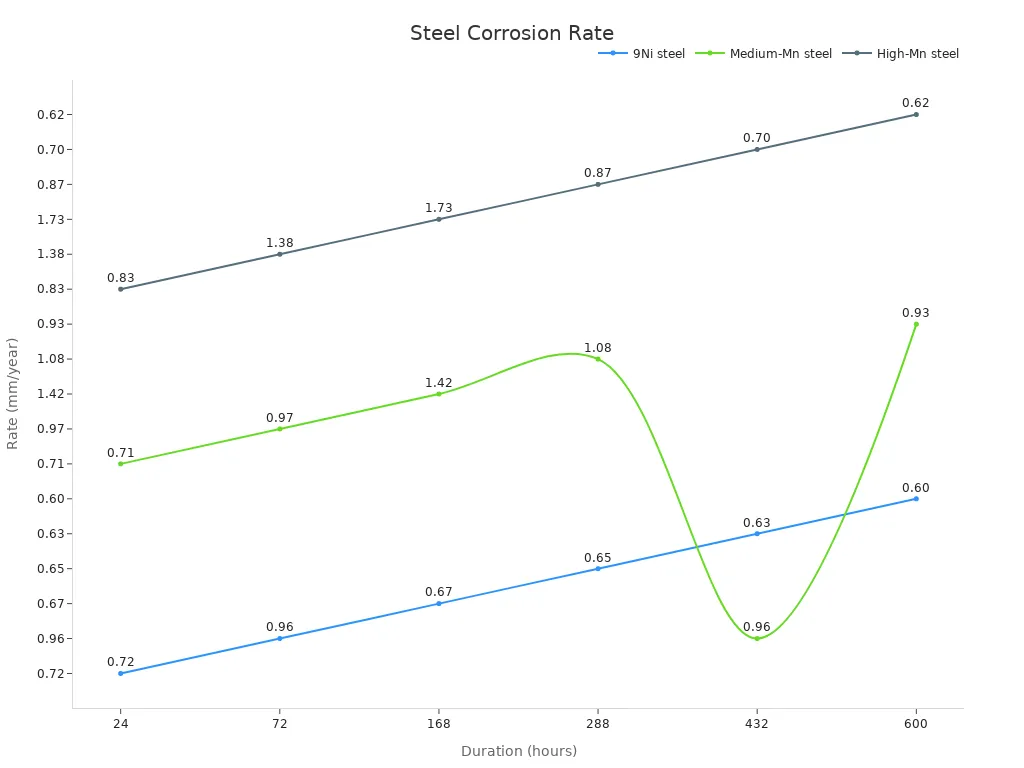
Manganese steel’s corrosion rate drops over time as a protective film forms. This helps it last longer, even in wet or salty places. Chromium-bearing manganese steels also slow down corrosion and reduce the risk of cracks from hydrogen.
Tip: For the best results in harsh environments, engineers choose manganese steel with added chromium or molybdenum and use special heat treatments.
Manganese Steel in Real-World Industrial Applications

Mining and Quarrying Equipment
Mining and quarrying put equipment through tough conditions. Workers use machines that crush, grind, and move heavy rocks every day. Manganese steel helps these machines last longer. Industry tests show that medium manganese steel, like Mn8/SS400, loses much less weight from wear than other steels. Over 300 hours, this steel lost about 69% less weight than traditional martensitic steels. Even though it is not the hardest, it absorbs more energy and stands up to impacts better. This means mining companies can use their equipment longer and spend less on repairs.
Tip: Manganese steel’s ability to get tougher when hit makes it perfect for jaw crushers, hoppers, and liners in mining.
Construction Machinery and Infrastructure
Construction sites need strong and safe equipment. Manganese steel gives both. It helps machines handle heavy loads and rough treatment. The table below shows how different types of manganese steel improve safety and durability in construction:
| Steel Type | Manganese Content (%) | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Hadfield Steel | 12 – 14 | High wear resistance, work-hardening |
| Carbon-Manganese Steel | Varies | Strong, tough, easy to weld |
Builders use low-carbon manganese steel for beams and columns. High-carbon types work best in heavy-duty machines. These steels keep their shape and strength, even when used every day. Construction companies choose manganese steel because it lasts long and keeps workers safe.
Transportation and Rail Industry
Trains and railways need materials that can handle constant stress. High-manganese cast steels, like Hadfield steel, work well in rail tracks and parts. These steels get harder as trains pass over them. Researchers found that adding chromium makes the steel even tougher and more stable. The steel’s microstructure changes during use, which helps it resist wear and damage. Rail companies trust manganese steel for its safety and long life. Computer models show that it stands up to the repeated loads from fast trains, keeping tracks safe and strong.
- High-manganese steels self-harden under heavy loads.
- Chromium boosts hardness and stability.
- Microstructure changes help resist wear and creep.
Note: Railways rely on manganese steel to reduce repairs and keep trains running safely.
Manganese Steel stands out in heavy industry. Companies see real benefits:
- High impact strength and wear resistance keep equipment running longer.
- Smart machining methods, like induction heating and carbide tools, boost productivity.
- Its toughness and work-hardening ability help absorb heavy impacts and resist wear.
FAQ
What makes manganese steel so tough?
Manganese steel gets tougher when it takes a hit. Its special mix of elements helps it resist dents and cracks, even in rough jobs.
Can you weld or cut manganese steel easily?
Welding and cutting manganese steel can be tricky. Workers use special tools and methods because the steel hardens as they work on it.
Where do people use manganese steel the most?
People see manganese steel in mining, railways, and construction. It works best in places where machines face lots of impact and wear.
Post time: Jun-19-2025